-
What is the role of Automotive Reliability Testing Standards?
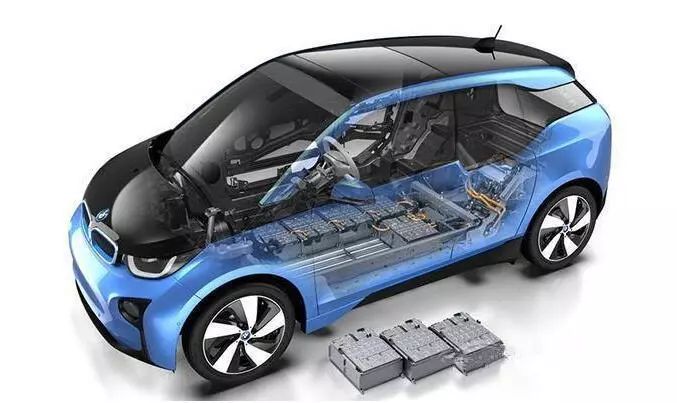
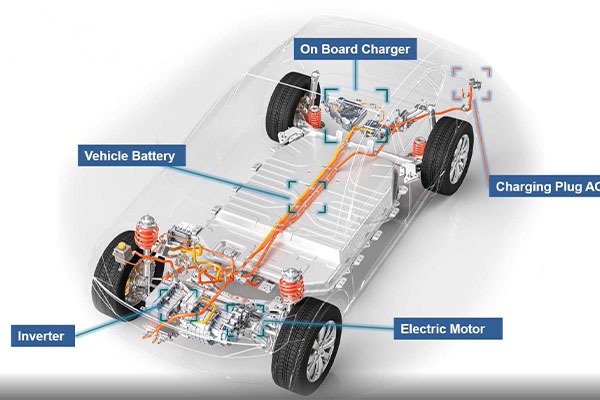
Automotive Reliability Testing Standards play a pivotal role in ensuring the dependability of key components, especially as China shifts its focus towards automotive excellence with new energy vehicles. Referred to as the “three electric,” comprising the motor, electronic control (electric drive), and battery, the success of this strategy hinges on the reliability of these components. To ensure their dependability, a suite of rigorous testing standards is in place, particularly focusing on temperature, humidity, and vibration aspects.
2. What are the Automotive Reliability Testing Standards?
- QC/T 413—2002 Basic technical conditions for automotive electrical equipment;
- GB/T 28046.3—2011 Environmental conditions and tests for electrical and electronic equipment of road vehicles – Part 3: Mechanical loads;
- GB/T 18488.1—2006 “Electric motor and controller for electric vehicles – Part 1: Technical conditions”;
- GB/T 18488.2—2006 “Electric motor and controller for electric vehicles – Part 2: Test methods”;
- GB/T 18488.1-2—2015 “Drive motor system for electric vehicles” (replaces GB/T 18488.1-2-2006);
- GB/T 29307—2012 “Reliability test method for electric vehicle motor system”;
- QC/T 893—2011 “Fault classification and judgment of drive motor system for electric vehicles”;
- QC/T 896—2011 “Interface for drive motor system of electric vehicles”;
- JEVS Z 107 Comprehensive test method for electric vehicle motor and controller;
- UL1004—1 General requirements for rotating electrical machines;
- IEC 69785 Rotating electrical machines for electric road vehicles (International Electrotechnical Commission);
- ECE R85 Net power of internal combustion engine or electric powertrain for driving M and N category vehicles;
- GB/T 2423.1—2008 Environmental testing for electric and electronic products – Part 2: Test method A: Low temperature;
- GB/T 2423.2—2008 Environmental testing for electric and electronic products – Part 2: Test method B: High temperature;
- GB/T 2423.3—2016 Environmental testing – Part 2: Test method Cab: Constant damp heat test;
- GB/T 2423.17—2008 Environmental testing for electric and electronic products – Part 2: Test method Ka: Salt mist;
- GB/T 2423.56—2006 Environmental testing for electric and electronic products – Part 2: Test method Fh: Broadband random vibration (digital control) and guidance;
- IS0 16750-3:2003 Road vehicles – Environmental conditions and tests for electrical and electronic equipment – Part 3: Mechanical environments;
- ISO 16750-3—2012 Road vehicles – Environmental conditions and tests for electrical and electronic equipment – Part 3: Mechanical loads;
- ISO 16750-4—2010 Road vehicles – Environmental conditions and tests for electrical and electronic equipment – Part 4: Climate environments;
- GB/T 29307—2012 Reliability test method for drive motor system of electric vehicles;
- IEC 60068-2-6—2007 Environmental testing – Part 2-6: Tests – Test Fc: Vibration (sinusoidal);
- IEC 60068-2-64—2008 Environmental testing – Part 2-64: Tests – Test Fh: Vibration, broadband random sampling;
- UN Transportation Testing (UNDOT 38.3) for Lithium Batteries 38.3 Lithium metal and lithium ion batteries;
- QC/T 742—2006 Lead-acid battery for electric vehicles;
- QC/T 743—2016 Lithium-ion battery for electric vehicles (2006, 2013);
- QC/T 744—2006 Metal hydride nickel battery for electric vehicles;
- ISO 12405-1-2011 Test specifications for lithium-ion traction battery packs and systems for electric road vehicles – Part 1: High-power applications;
- IS0 12405-1 /-2/3 (1 and 2 were issued and implemented in 2011 and 2012, 3 was formally issued in 2013);
- IEC 62660-1/-2/-3 (1 and 2 were formally implemented in 2010);
- SAE J2380—2013 Vibration test for electric vehicle batteries.
- 32.GMW 16390 General Specificationfor Analysis/Development/Validation (A/D/V) of Rechargeable Energy StorageSystems (RESS);
- 33.SAND 2005-3123 Energy-ApplicationsElectrical Energy System Abuse Test Manual for Electric and Hybrid ElectricVehicle Applications。
3. What are the motor and electric drive testing standards and related content?
1) Sinusoidal Vibration Testing:
– QC/T 413-2002: Requires the motor to withstand 8 hours of frequency sweep vibration in the X, Y, and Z directions.
– ISO16750-3: Specifies frequency sweep vibration testing in the X, Y, and Z directions.
– QC/T 413-2002 Parameters: Vertical Z direction (10-25Hz, amplitude 1.2mm, peak-to-peak 2.4mm; 25-500Hz, acceleration 30m/s2). Horizontal X, Y directions (10-25Hz, amplitude 0.6mm; 25-500Hz, acceleration 15m/s2). Each direction tested for 8 hours.
2) Random Vibration Testing:
– GB/T28046.3-2011: Requires the motor to undergo random vibration testing in the X, Y, and Z directions.
– GB/T18488.1~2-2015: Additional standards for random vibration testing.
3) Temperature and Humidity Testing:
– Low Temperature Storage/Operation: Performed according to GB/T2423.1 and GB/T2423.2 standards.
– High Temperature Storage/Operation: Conducted according to GB/T2423.2.
– Damp Heat Testing: Performed in accordance with GB/T2423.3.
4) Salt Spray and Environmental Adaptability Testing:
– Salt Spray Testing: As per GB/T2423.17 standards.
– Environmental Adaptability Testing: Refer to GB/T 18488.1~2-2015.
5) Reliability Testing:
– GB/T 29307-2012: Comprehensive reliability testing for the drive motor system of electric vehicles.
4. Battery Testing Standards:
1) Vibration Testing:
– UN 38.3: Specifies vibration frequencies of 7-200Hz for X, Y, and Z axes.
– IS012405-1: Requires vibration testing within a frequency range of up to 200Hz for X, Y, and Z axes.
2) Random Vibration Testing:
– Three-Axis Composite (SAE J2380): Combines vibration, temperature, and operating conditions with random vibration frequencies of 10-190Hz.
Three-Axis Composite (GMW16390):
– Uses a wide frequency range of 8-1000Hz for vibration testing in the X, Y, and Z axes, with each axis subjected to 24 hours of vibration.
3) Temperature Requirements:
– High and Low-Temperature Testing: Governed by specific temperature ranges and cell temperature constraints.
For Further Insights and Comprehensive Testing Solutions, Visit Linkotest(www.linkotest.com).










Leave A Comment